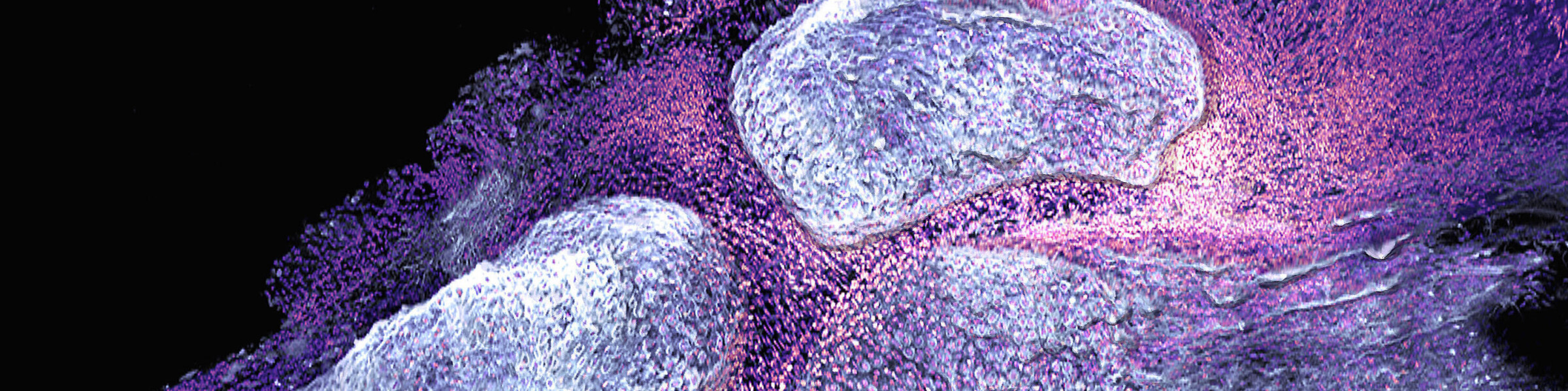
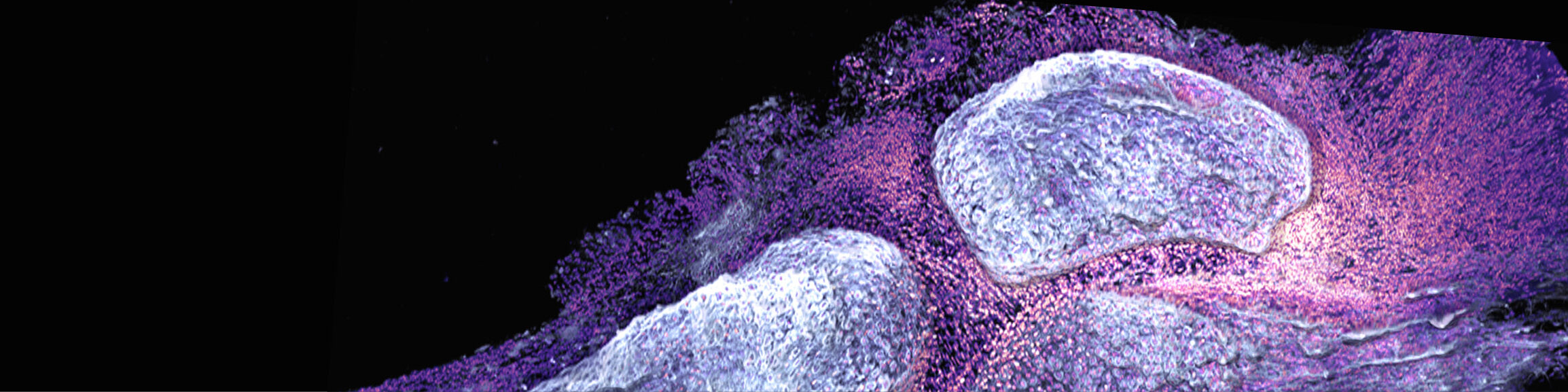
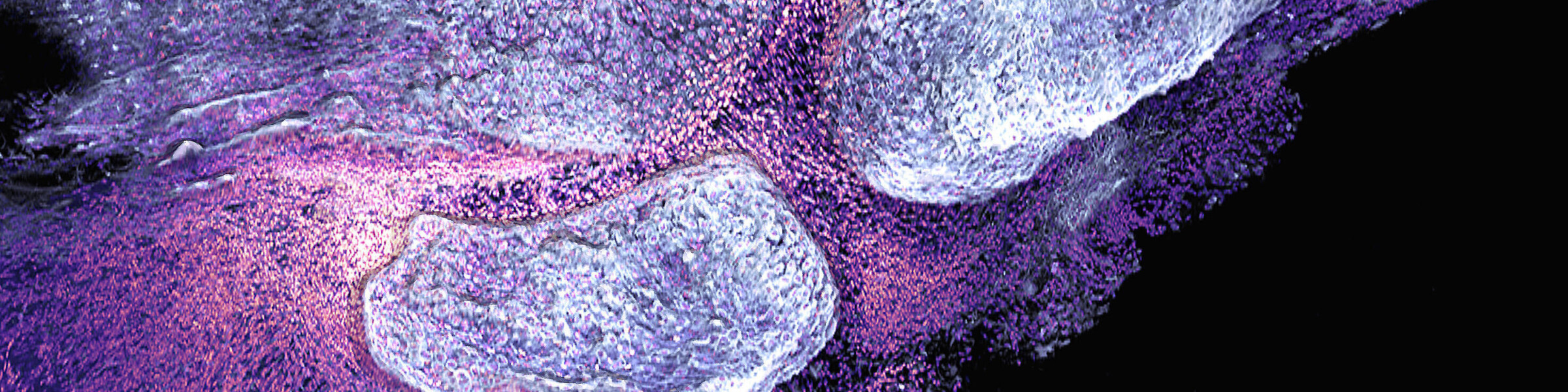
Such factors include the products of resident cells that are located in the vicinity of osteoclasts, such as fibroblasts, adipocytes and neutrophils/eosinophils, which undergo a functional change during inflammation and thereby influence osteoclasts. This process creates a functional inflammatory niche that instructs osteoclasts and osteoblasts within the microenvironment which influences bone homeostasis.