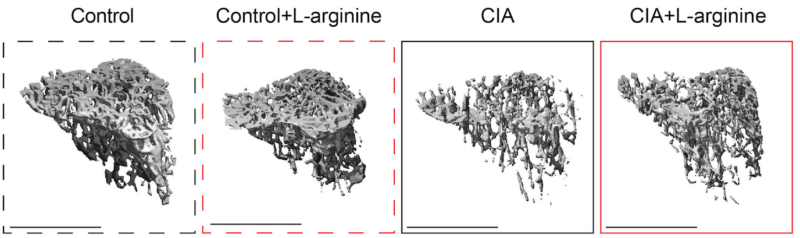
This research project explores the potential of L-arginine supplementation as a new treatment for bone loss caused by chronic inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Preliminary findings indicate that L-arginine can reduce inflammation and bone erosion in mouse models of arthritis. The project aims to uncover the molecular mechanisms by which L-arginine affects bone health, focusing on its role in inhibiting pro-inflammatory cells and promoting bone formation. By studying both animal models and RA patients, researchers hope to develop effective therapeutic strategies to prevent and treat inflammation-induced osteoporosis.
Section B Project B05
Arginine supplementation as new therapeutic option against inflammatory bone loss
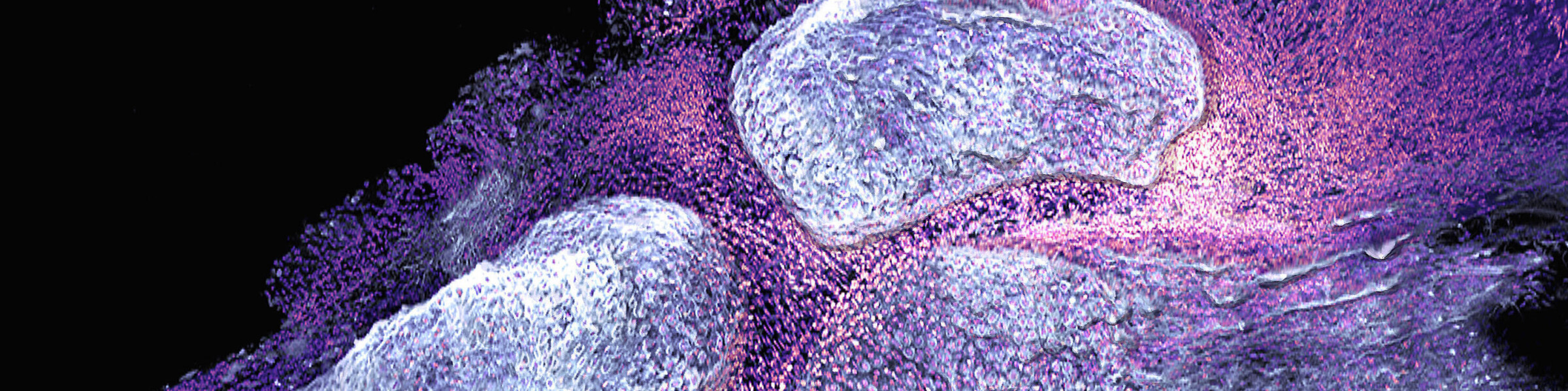
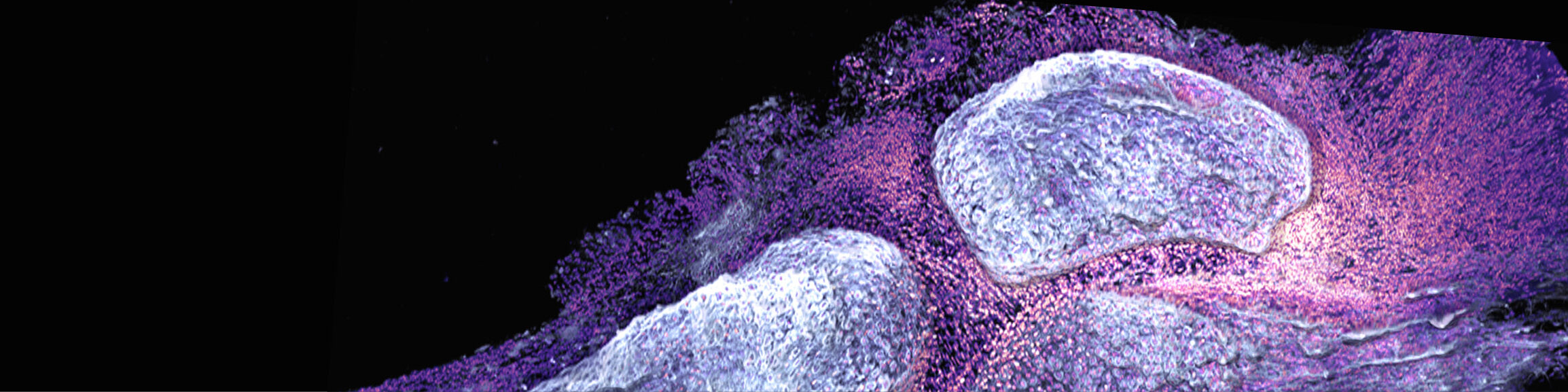
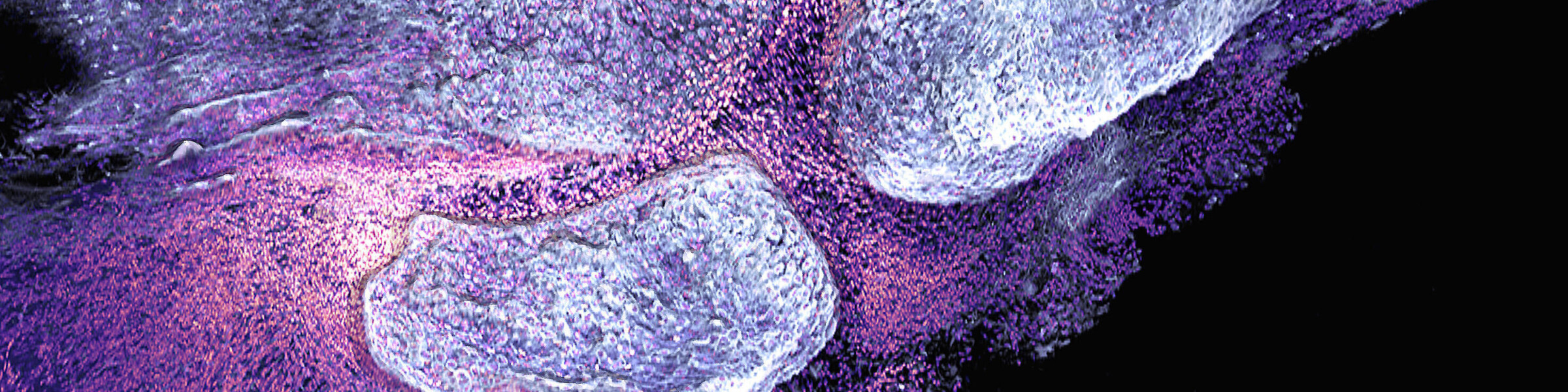
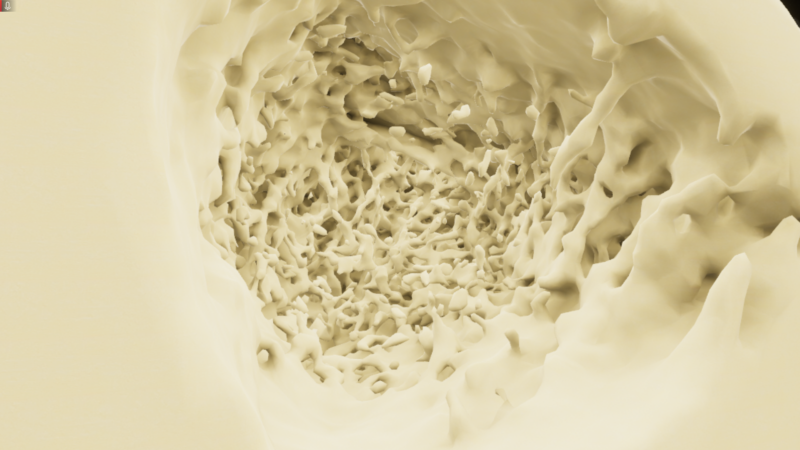
Arginine is a key amino acid that controls macrophage metabolism and function. In myeloid and other cells, arginase conveys L-arginine into urea and ornithine. Treatment with L-arginine inhibits inflammation by re-polarization of macrophages into anti-inflammatory alternative activated macrophages (Hannemann, et al., 2019). In this project, we want to test the ability of arginine and its metabolites to inhibit osteoclastogenesis and block inflammatory bone loss. Our goal is to elucidate the outcome of L-arginine supplementation in protective and therapeutic application during arthritis development as well as to define the importance of L-arginine catabolic enzymes such as arginase-1 and/or -2 expression in myeloid cells. Such approach would allow protection against bone loss by inhibition of inflammation and a metabolic reprogramming of the macrophages and osteoclasts. In the long-term perspective, we plan to analyze the effect of dietary L-arginine supplementation on bone loss in RA patients.